Yeast Infection Treatment: Safe, Effective Options for Long-Term Relief
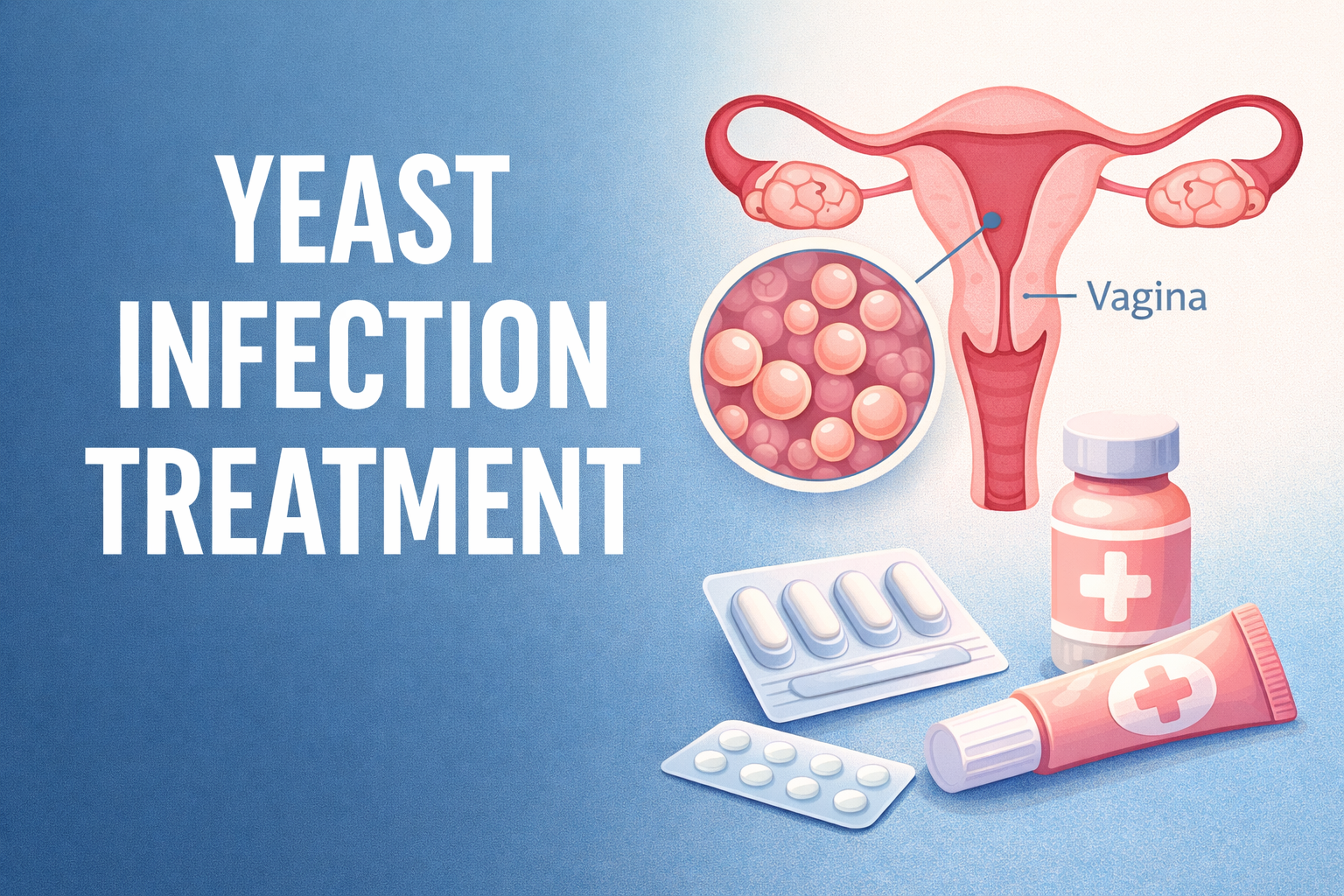
Yeast infections are a common health concern affecting millions of people worldwide each year. While they are often uncomfortable, the good news is that yeast infections are highly treatable with the right medical guidance and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding available yeast infection treatment options can help individuals manage symptoms effectively, prevent recurrence, and protect overall health.
This comprehensive guide explores yeast infection treatment methods, including over-the-counter remedies, prescription medications, home care strategies, and prevention tips—while maintaining a medically accurate and advertiser-friendly approach.
What Is a Yeast Infection?
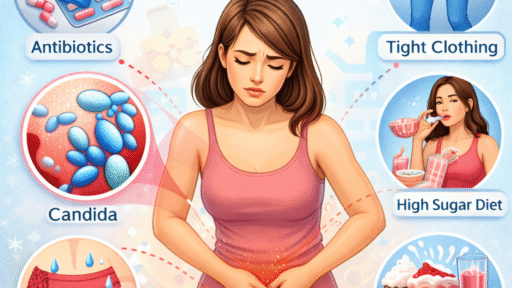
A yeast infection is typically caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a naturally occurring fungus found in the body. Under normal circumstances, healthy bacteria keep yeast levels balanced. However, factors such as antibiotics, hormonal changes, weakened immune systems, or uncontrolled blood sugar levels can disrupt this balance, leading to infection.
Yeast infections can occur in various parts of the body, including the mouth, skin, digestive tract, and vaginal area. This article focuses on general yeast infection treatment strategies rather than graphic or explicit details.
Common Symptoms That May Require Treatment
Symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common signs that may prompt treatment include:
-
Persistent itching or irritation
-
Redness or swelling in the affected area
-
Discomfort during daily activities
-
Changes in discharge or skin texture
-
Burning sensations
It is important to consult a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, as symptoms can overlap with other conditions.
Over-the-Counter Yeast Infection Treatments
Many mild yeast infections can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal medications. These products are widely available at pharmacies and are often the first line of treatment.
Common OTC Options
-
Antifungal creams and ointments
-
Vaginal suppositories (for applicable cases)
-
Antifungal tablets designed for external use
OTC treatments typically contain antifungal agents that stop yeast growth and help restore balance. Treatment duration can range from one to seven days, depending on the product and severity.
Important note: Even with OTC options, reading labels carefully and following instructions is essential for safety and effectiveness.
Prescription Yeast Infection Treatments
For moderate to severe infections, or cases that do not respond to OTC products, prescription treatments may be necessary.
Prescription Options May Include:
-
Oral antifungal medications
-
Stronger topical antifungal treatments
-
Extended-duration treatment plans for recurrent infections
Prescription treatments are often recommended for individuals experiencing frequent yeast infections or those with underlying health conditions such as diabetes or immune disorders.
Yeast Infection Treatment for Recurrent Cases
Recurrent yeast infections are typically defined as four or more infections within a year. These cases often require a long-term management approach.
Long-Term Treatment Strategies
-
Maintenance antifungal therapy
-
Identifying and managing underlying triggers
-
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider
Addressing contributing factors such as blood sugar control, medication use, and lifestyle habits can significantly reduce recurrence.
Lifestyle and Hygiene Practices That Support Treatment
In addition to medication, lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in yeast infection treatment and prevention.
Helpful Practices Include:
-
Wearing breathable, moisture-wicking clothing
-
Avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use
-
Maintaining good hygiene without over-cleansing
-
Managing stress levels
-
Supporting immune health through nutrition
These practices help create an environment that discourages yeast overgrowth.
Diet and Yeast Infection Management
While diet alone cannot cure a yeast infection, it can support treatment and overall health.
Dietary Considerations
-
Limiting excess sugar intake
-
Eating balanced meals rich in fiber
-
Staying hydrated
-
Including probiotic-rich foods if recommended by a healthcare professional
Dietary changes should complement—not replace—medical treatment.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Medical advice should always be sought if:
-
Symptoms persist despite treatment
-
Infections recur frequently
-
Symptoms are severe or worsening
-
The individual is pregnant, immunocompromised, or managing chronic illness
Professional evaluation ensures proper diagnosis and safe treatment selection.
Prevention: Reducing the Risk of Future Infections
Preventive strategies are an important part of yeast infection treatment planning.
Prevention Tips
-
Follow prescribed treatments fully
-
Avoid unnecessary use of scented personal products
-
Maintain balanced nutrition and hydration
-
Attend routine medical checkups
Prevention not only reduces discomfort but also lowers long-term healthcare costs.
Final Thoughts on Yeast Infection Treatment
Yeast infections are common, manageable, and treatable with the right approach. Whether using over-the-counter remedies, prescription medications, or supportive lifestyle changes, the key to effective treatment lies in accurate diagnosis and consistent care.
By focusing on evidence-based treatment options and professional medical guidance, individuals can achieve lasting relief while protecting their overall health.



Heard some buzz about thacasino. Gonna check it out. Heard their games are kinda slick and the bonuses decent. Hope it’s legit! thacasino
myHealth topic points” is not a standardized phrase but appears to refer to health and wellness topics or points within a specific program or online portal named “MyHealth” (e.g., MyHealth Rewards, MyHealth Alberta, or myHealth.gov.mt).
Thank you for this clear overview of Diabetes Mellitus. It’s very helpful to see the breakdown of symptoms and causes in one place. Managing blood sugar is such a vital part of long-term health.”