Diabetes Symptoms: A Complete Guide to Understanding Early Warning Signs
Diabetes is one of the most common long-term health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. While only a healthcare professional can diagnose diabetes, understanding the early and common symptoms is essential for recognizing when to seek medical advice. Early awareness can support better health decisions, lifestyle adjustments, and timely evaluation by a doctor.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of general diabetes symptoms, how they appear, why they matter, and when to seek medical help. It does not provide diagnosis, treatment, or medical instructions—its purpose is informational and educational.
What Is Diabetes? (Brief Overview)
Diabetes is a health condition related to how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Normally, the body uses glucose for energy, and a hormone called insulin helps move glucose into cells. When this process doesn’t work properly, blood sugar levels can rise.
The three main types include:
-
Type 1 diabetes
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Gestational diabetes (occurs during pregnancy)
Although symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity, many people share similar early warning signs.
Why Recognizing Symptoms Matters
Symptoms of diabetes can start slowly and may be easy to overlook at first. Many people experience mild changes and assume it’s related to stress, diet, or daily routines. However, identifying symptoms early and consulting a professional can help prevent complications and promote healthier long-term management.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Below are some of the most widely reported symptoms associated with diabetes. These are general indicators, not a diagnosis. Many of these can also be related to other health issues.
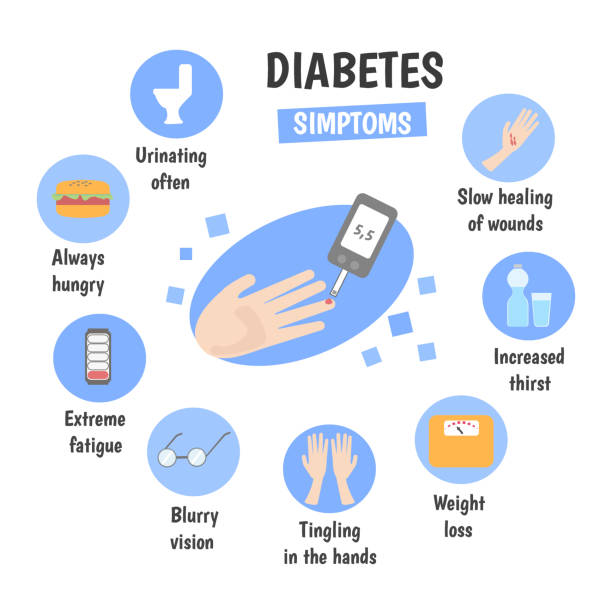
1. Increased Thirst (Polydipsia)
One of the most common symptoms people notice is feeling unusually thirsty. When blood sugar levels rise, the body may attempt to maintain balance by drawing fluid from tissues, leading to increased thirst.
People may feel:
-
thirsty even after drinking
-
dryness in the mouth
-
an urge to drink more frequently than usual
2. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
Frequent urination is closely connected to increased thirst. When there is excess glucose in the bloodstream, the kidneys work harder to filter it out, which may lead to urinating more often—especially during the night.
3. Increased Hunger (Polyphagia)
Some people experience increased hunger because the body is not using glucose effectively for energy. This may cause the brain to signal a need for more food, even shortly after eating.
4. Unexplained Weight Changes
Weight changes—especially unintentional weight loss—may occur in some individuals. This is more common in people with Type 1 diabetes but can appear in others as well.
The body may start breaking down fat or muscle for energy when glucose isn’t entering cells effectively.
5. Fatigue and Low Energy Levels
Feeling tired is one of the most common symptoms. When the body cannot use glucose properly, cells lack the energy they need, causing persistent fatigue.
People may notice:
-
tiredness after meals
-
general weakness
-
difficulty concentrating
6. Blurred Vision
Fluctuating fluid levels in the body may temporarily affect the eyes’ ability to focus, leading to blurred or hazy vision. This can occur in one or both eyes and may come and go as glucose levels change.
7. Slow-Healing Wounds
Some individuals notice that cuts, bruises, or infections take longer than usual to heal. High blood sugar can affect circulation and the body’s natural healing processes.
8. Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet
Nerve-related symptoms—such as tingling, numbness, or a “pins and needles” feeling—may occur in some people. This tends to happen when high blood sugar affects nerve function over time.
9. Frequent Infections
People may experience recurring infections such as:
-
skin infections
-
gum infections
-
urinary tract infections
This happens because consistently high glucose can affect the body’s natural ability to defend itself.
10. Dry Skin or Itching
Changes in circulation, hydration, or moisture levels in the body may lead to dry or itchy skin. This symptom alone is not specific to diabetes but can appear along with other signs.
Symptoms Specific to Women
Some women may notice:
-
increased urinary discomfort
-
higher likelihood of yeast infections
-
fatigue during hormonal changes
These symptoms can result from elevated glucose levels that create an environment which supports certain yeast or bacterial growth.
Symptoms Specific to Men
Some men may experience:
-
low energy
-
reduced muscle strength
-
increased thirst or hunger
-
frequent urination
These symptoms are general and can be caused by various factors, not just diabetes.
Symptoms Related to Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and may not always show obvious symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
-
increased thirst
-
fatigue
-
frequent urination
Because pregnancy naturally causes changes in thirst and urination, regular prenatal checkups are the safest way to detect gestational diabetes.
Mild vs. Severe Symptoms
Mild symptoms may include:
-
being a little more thirsty
-
feeling tired
-
occasional blurry vision
More noticeable symptoms may include:
-
frequent urination
-
sudden weight changes
-
slow-healing wounds
Again, only a healthcare provider can determine the cause.
When to See a Healthcare Professional
It’s a good idea to talk to a professional if you notice:
-
multiple symptoms occurring at the same time
-
persistent changes in energy levels, thirst, or urination
-
strong family history of diabetes
-
sudden vision changes
-
unexplained weight loss
A doctor may perform blood tests to check glucose levels and provide proper guidance.