Vaginal Yeast Infection: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment Options, and Prevention
A vaginal yeast infection is a common health condition that affects many women at some point in their lives. While it can be uncomfortable, it is generally manageable with proper care and medical guidance. Understanding what a vaginal yeast infection is, why it occurs, and how it is commonly treated can help individuals make informed decisions and seek appropriate support when needed.
This article provides a comprehensive, educational overview of vaginal yeast infections, including symptoms, potential causes, treatment approaches, and preventive strategies. The information shared here is for general informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
What Is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
A vaginal yeast infection, also known as vaginal candidiasis, occurs when there is an overgrowth of yeast in the vaginal area. Yeast is a type of fungus that normally lives in small amounts in the body, including the vagina, without causing harm.
When the natural balance of microorganisms in the vagina is disrupted, yeast can multiply more than usual, leading to symptoms. Vaginal yeast infections are common and can affect individuals of different ages and lifestyles.
Common Symptoms of a Vaginal Yeast Infection
Symptoms may vary from person to person, but common signs of a vaginal yeast infection can include:
-
Vaginal itching or irritation
-
Redness or swelling in the vaginal area
-
Thick, white vaginal discharge
-
Discomfort during urination
-
A burning or uncomfortable sensation
Not everyone experiences all symptoms, and symptom severity can differ.
What Causes Vaginal Yeast Infections?
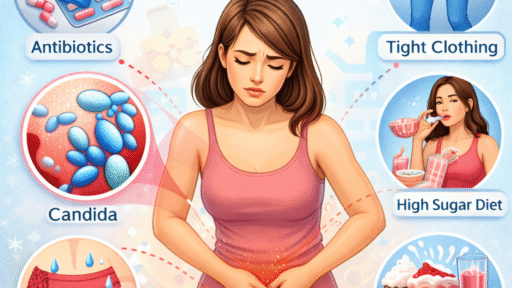
Several factors can contribute to the development of a vaginal yeast infection by altering the vaginal environment.
1. Changes in Vaginal Balance
The vagina naturally maintains a balance of bacteria and yeast. Disruptions to this balance may allow yeast to grow excessively.
2. Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics may reduce beneficial bacteria that help control yeast levels, potentially increasing the risk of yeast overgrowth.
3. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy or hormonal therapy, may influence yeast growth.
4. Immune System Factors
A weakened immune system may make it more difficult for the body to regulate yeast levels effectively.
5. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Moist environments, tight clothing, and prolonged dampness may contribute to conditions that allow yeast to thrive.
Who Is More Likely to Experience Yeast Infections?
Vaginal yeast infections can affect many individuals, but some may be more susceptible due to:
-
Hormonal changes
-
Frequent antibiotic use
-
Certain medical conditions
-
Lifestyle factors
Understanding personal risk factors can help with prevention and early recognition.
How Vaginal Yeast Infections Are Typically Diagnosed
Diagnosis is usually made by a healthcare professional based on symptoms and, in some cases, a physical examination or laboratory testing. Because symptoms may resemble other conditions, professional evaluation helps ensure accurate identification and appropriate care.
Self-diagnosis may not always be reliable, especially for individuals experiencing symptoms for the first time or recurrent infections.
Treatment Options for Vaginal Yeast Infections
Treatment for vaginal yeast infections depends on symptom severity, frequency, and individual health factors.
1. Over-the-Counter Treatments
Some yeast infections are treated with non-prescription antifungal products designed for vaginal use. These products are commonly available in pharmacies.
2. Prescription Treatments
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications when symptoms are more severe, persistent, or recurring.
3. Professional Medical Guidance
For individuals experiencing frequent or complicated infections, professional evaluation helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment duration and type vary based on individual needs and medical advice.
Managing Recurrent Yeast Infections
Some individuals experience yeast infections more than once. Recurrent infections may require additional evaluation to identify underlying contributing factors.
Management strategies may include:
-
Reviewing medical history
-
Adjusting lifestyle habits
-
Following a healthcare provider’s long-term care plan
Addressing underlying factors can reduce recurrence.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures may help reduce the likelihood of developing a vaginal yeast infection. General recommendations include:
-
Maintaining proper hygiene
-
Wearing breathable clothing
-
Avoiding prolonged moisture
-
Following medical guidance regarding medications
-
Supporting overall wellness
Preventive habits can support vaginal health and balance.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Medical evaluation is recommended if:
-
Symptoms are severe or persistent
-
Infections recur frequently
-
Symptoms do not improve with standard care
-
The diagnosis is uncertain
Professional guidance ensures safe and effective care.
Vaginal Yeast Infections and Overall Wellness
Vaginal health is an important part of overall wellness. Understanding normal changes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking care when needed supports long-term health and comfort.
Education and awareness help individuals approach this common condition with confidence and clarity.
Myths and Misunderstandings
Myth 1: Yeast infections are uncommon
They are actually quite common and affect many individuals at least once.
Myth 2: Poor hygiene is always the cause
Yeast infections are often related to internal balance changes rather than hygiene alone.
Myth 3: They always require the same treatment
Treatment depends on individual symptoms and medical history.
Final Thoughts
Vaginal yeast infections are common and manageable with proper awareness, care, and medical guidance. Understanding symptoms, potential causes, and treatment options empowers individuals to make informed decisions and seek support when needed.
While the condition can be uncomfortable, effective care and preventive strategies help support long-term vaginal and overall health.